

Any time owners make a change to the title of real estate, they must record a deed with the County Recorder. This Step-by-Step guide outlines the requirements and provides samples with instructions.
PCOR Tips: All recorded forms must be accompanied by a PCOR (Preliminary Change of Ownership Report). This guide has links to the form and tips on filling it out.
Affidavits of Death: If you are transferring Joint Tenancy property, Community Property with Rights of Survivorship, or Transfer on Death Deed property because someone has died, use the Affidavits of Death guide instead of this one.
California mainly uses two types of deeds: the “grant deed” and the “quitclaim deed.” Most other deeds you will see, such as the common “interspousal transfer deed,” are versions of grant or quitclaim deeds customized for specific circumstances. Since the interspousal deed is so commonly requested, we are including a sample in this guide.
A grant deed is used when a person who is on the current deed transfers ownership or adds a name to a deed. The grantor(s) promise that they currently own the property and that there are no hidden liens or mortgages.
A quitclaim deed (sometimes misspelled “quick claim”) is used when someone gives up (waives or disclaims) ownership rights in favor of another person. The grantor may or may not be on the current deed. A quitclaim deed is often used in divorces or inheritance situations, when a spouse or heir gives up any potential rights to real estate. The grantor is giving up their own rights, if any, but not promising anything else.
An interspousal deed is used between spouses or registered domestic partners (“DP”) to change real estate to or from community property. Spouses/DPs can use grant or quitclaim deeds to do the same things, but the interspousal deed makes it clear that the transaction is intended to affect community property rights.
There are many other types of deeds, such as warranty deed, joint tenancy deed, easement deed, trust deed, etc. In some states, these may be considered separate deed types, but in California, these are usually just customized grant deeds.
In a warranty deed, the grantor promises to pay for any lawsuits or damages due to undisclosed ownership disputes. In California, title insurance usually covers such disputes.
Other types of deeds, such as joint tenancy deeds, corporation deeds, easement deeds, or mineral rights deeds, can be created by customizing our grant deed format by downloading the RTF (word processing) version from our website. Consult an attorney or come to the Law Library to research appropriate wording.
You will need information from the current deed. If you need a copy of the current deed, contact the Recorder’s Office where the property is located. In Sacramento, call (916) 874-6334.
To transfer ownership, disclaim ownership, or add someone to title, you will choose between a “grant deed” and a “quitclaim deed.” Spouses/domestic partners transferring property between each other may choose an “interspousal deed.”
Here is a flow chart to help you choose:
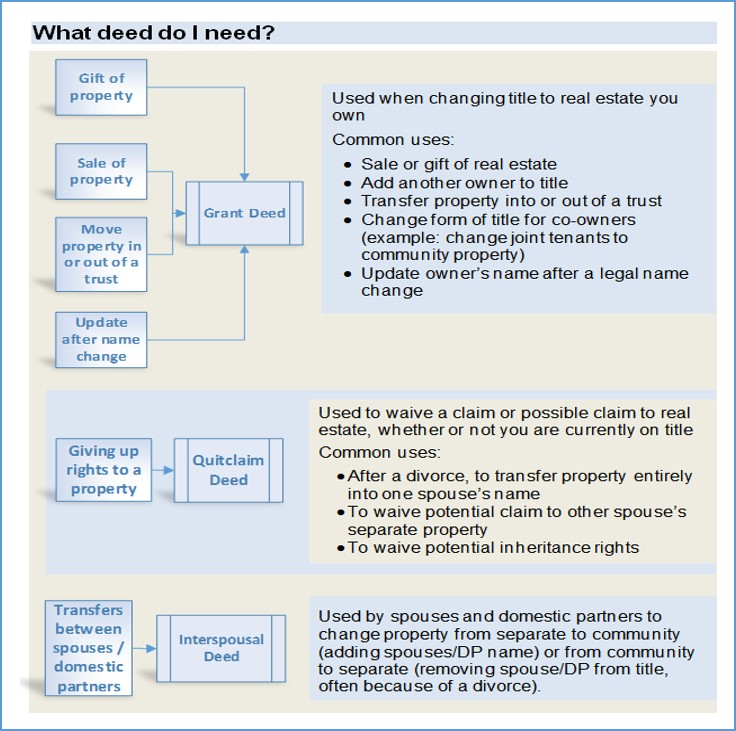
If there is more than one new owner, you are moving the real estate into or out of a trust, or the new owner is married, the form of title can have important effects.
If there is only one new owner, and that person is unmarried, title can usually be left blank, although it doesn’t hurt to state something like “a single person” or “a widow” or the like.
If you leave this blank, the default is “tenants in common.”
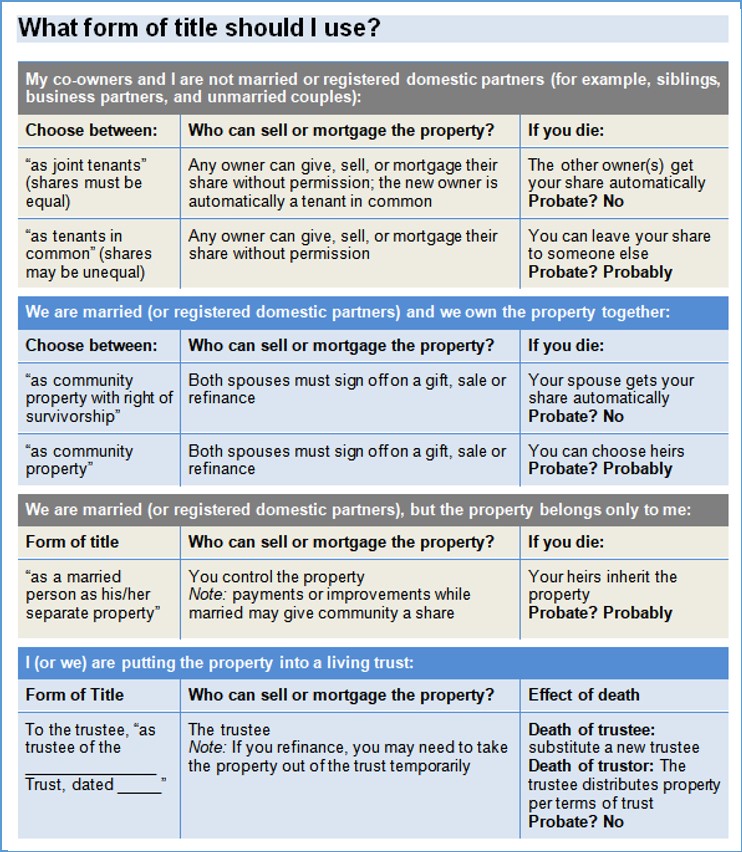
Examples: siblings who inherit property together, business partners, couples who are not married or registered domestic partners (DP).
If you leave the title line blank, or fill in something like “as husband and wife” or “as domestic partners,” it will be treated as “community property” and a share will go to any heirs instead of all to the surviving spouse/DP.
If only one spouse/DP owns the property (because that person already owned it when they got married, or it was a gift or inheritance), they can make that clear by using the phrase “a married man/woman/person as his/her/their sole and separate property.” Note: if any money earned during the marriage is spent to purchase, make mortgage payments, maintain, or improve the house, the community owns a share regardless of what it says on the deed.
Many couples use trusts to hold their property. The contents of a trust are technically owned by the trustees. Therefore, when transferring property into a trust, the grantees are the “[name of trustees], as trustees of the [name of trust] dated [date trust was signed].”
When transferring property out of a trust, the grantors are the trustees, identified the same way.
See “Forms of Title for Multiple Owners,” below, for examples of how these are entered onto the deed.
Your choice of title can have many effects later, such as when you sell or refinance, if one owner falls into debt, if one owner dies, or if a couple divorces. Some examples of potential effects are:
If you have questions about which form of title to use, talk to a family or estate lawyer or research your options at the law library.
You will find filled-out samples of each type of deed at the end of this guide.
The deed can be filled out online, typed, or neatly written in dark blue or black ink. You will need the following information:
The notary will charge a fee for this service. You can find notaries at many banks, mailing services, and title companies.
The new owners do not need to sign.
The PCOR is required when property changes hands, to update the tax records. Turn it in at the Recorder’s Office along with the deed. You can download a Sacramento version of the PCOR from Cal Assessor e-Forms. Each county has its own version; contact the assessor’s office in the county where the property is located to obtain the proper form.
The Recorder’s Office charges a recording fee (currently $20/first page plus $3 for additional pages). Current Sacramento fees are available at the County Clerk/Recorder’s website. You may also need to pay the Documentary Transfer Tax or a $75 “Building Homes and Jobs Act” fee.
When property changes hands, it is reassessed for tax purposes, often causing a sizeable increase in property tax for the new owner.
Certain transfers are excluded from reassessment, including:
If your transfer is excluded from reassessment, you may need to file a claim with the County Assessor. For more information in Sacramento, call the Assessor’s office (916‑875-0750) or visit the Sacramento Assessor’s office website.
Some parts of deeds often need more explanation.
When property changes hands, the county charges a one-time tax of $.55 per $500 of the value of the real estate (1.1%). Some kinds of transfers are exempt. If yours is exempt, enter the Revenue and Taxation code that provides the exemption, and an explanation, then sign. If yours is not exempt, calculate the dollar amount and write it in.
Common exemption codes and explanations:
Other exemptions may be available. See the list of “Transfer Tax Exemptions” on the Sacramento Recorder’s website.
There is an additional $75 fee on mortgage refinances and other real estate transactions that are exempt from Documentary Transfer Tax. Some exceptions apply. Contact your county recorder’s office to determine the total amount you will need to pay.
Grantor(s): The current owner or person transferring the property rights or part of the property rights. This is the person or people who will sign this deed.
Grantee(s): List all people who are receiving property rights from the grantor(s). If the grantor is staying on title, be sure to list the grantor’s name as one of the grantees also.
It’s often helpful to include the grantors’ and grantees’ marital status.
When there is more than one grantee, you will need to specify the form of title. It can also be helpful to do that if a grantee is a married person or domestic partner.
Here are examples of common title phrases:
Here is a quick reference chart comparing common forms of title.
If you change your name (by court-ordered name change, marriage, or divorce), deeds made out to your old name should be updated. Make out a new grant deed from yourself ([new name], who acquired title under the former name [old name]) as Grantor to yourself ([new name]) as Grantee. For example:
 language used to update a deed when a name has changed: Grantor Chris Jones, who acquired title under the former name Chris Smith, grants to Chris Jones." width="881" height="167" />
language used to update a deed when a name has changed: Grantor Chris Jones, who acquired title under the former name Chris Smith, grants to Chris Jones." width="881" height="167" />
In some situations, after a property owner dies, a new owner receives the property without having to go through probate, just by recording an affidavit. Common examples include people who own the property together as joint tenants or community property with right of survivorship, and people who inherit property via a transfer on death (TOD) deed. For more information, see our guide on Affidavits of Death: Transferring Property without Probate.
The new owner removes the prior owner from the deed by filing an Affidavit of Death of Joint Tenant, Affidavit of Surviving Spouse, or Affidavit of Death of Transferor under TOD Deed.
This is legally sufficient to change ownership, but the lack of a deed showing the new owner’s name can be confusing and lead to problems when selling or refinancing the property. The new owners can make the chain of title (history of ownership) clearer by recording a Grant Deed showing themselves as the Grantee. Here’s how:
Fill out a standard Grant Deed for the property. The new owner will list themselves as both the Grantor and the Grantee. For example, if Chris Jones was a surviving joint tenant on property, after they recorded an Affidavit of Death of Joint Tenant, they could fill out a grant deed like this:
 language used to create a Grant Deed for property you now own after filing an affidavit of death of joint tenant or other similar affidavit. The Grant Deed lists the new owner as both the grantor and grantee. This helps clarify the chain of title." width="1024" height="229" />
language used to create a Grant Deed for property you now own after filing an affidavit of death of joint tenant or other similar affidavit. The Grant Deed lists the new owner as both the grantor and grantee. This helps clarify the chain of title." width="1024" height="229" />
This is the full description of the property, not just the address. It may be brief or very long and full of legalese. It must match the current deed exactly.

You may want to photocopy the legal description and attach it to the new deed as an exhibit, especially if it is too long to fit on the page.

If a piece of real estate is part of a probate case, once the case is resolved the personal representative (executor or administrator) must record documentation showing that it is now owned by the heir or heirs. They can either:
Because the Order is bulky and may have personal and financial information, recording a deed is often preferred. The deed must reference the legal description of the property, the county and case number of the probate case, and the date and title of the order authorizing distribution, state that there is no representation, warranty, or covenant of any kind, and be signed by the personal representative “as executor or administrator of the Estate of ________.”
Here is example wording of a Deed to Real Property that can be customized to fit your needs. The sample is worded for a probate that includes a will. If your situation does not include a will, you would state that you are “administrator of the estate” instead of “executor of the will.”

DivorceNet: “Interspousal Transfers vs Quitclaim Deed”
Self-help information about the differences between these two deeds.
Deeds for California Real Estate (KFC 170 .Z9 R36, Self-Help)
This book, published by Nolo Press, a respected publisher of self-help legal books, is a guide to choosing the right kind of deed, completing the required forms, and filing them. It also discusses related legal issues such as disclosure requirements, community property issues, and tax and estate planning. It contains forms for most transfers of property.
Miller & Starr California Real Estate Forms (KFC 140 .M53)
Sections 1:133-1:137 offer language for grant, interspousal, quitclaim, and easement deeds.
California Real Property Practice Forms Manual (KFC140 .A65 C34)
A range of sample forms for specific situations such as easements, mineral rights, and more.
PCOR Instructions and Tips
In addition to your deed, you will also need to turn in a PCOR (Preliminary Change of Ownership Report). Download the Sacramento PCOR or obtain it from the county assessor where the property is located (the form is different in each county).
Below are samples of the deeds discussed in this guide.

 Sample Quitclaim Deed" width="1406" height="1819" />
Sample Quitclaim Deed" width="1406" height="1819" />

This material is intended as general information only. Your case may have factors requiring different procedures or forms. The information and instructions are provided for use in the Sacramento County Superior Court. Please keep in mind that each court may have different requirements. If you need further assistance consult a lawyer.